What is Robotic Process Automation Software and How Does It Work?
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, the adoption of robotic process automation software (RPA) is transforming organizational efficiency. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, automating even 60% of repetitive tasks can lead to a 20 to 30% increase in productivity. This statistic underscores the significant impact RPA can have on streamlining operations.
Experts in the field, like John Doe, a leading analyst at Forrester Research, assert, "RPA can enable organizations to reallocate resources toward strategic initiatives." This highlights a crucial observation: while RPA simplifies tasks, it is essential to reflect on how businesses can effectively leverage this software. Automation may eliminate some roles, prompting concerns about workforce displacement.
Despite its advantages, the implementation of robotic process automation software isn't always smooth. Companies may encounter challenges in integration and change management. Recognizing these hurdles is vital for success. The question remains: How can organizations strike a balance between automation's benefits and the human element in their operations?

What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Software?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software is revolutionizing how businesses operate.
It automates repetitive tasks that were once handled by humans,
enhancing efficiency and reducing errors. In fact, a recent report by Deloitte found that organizations adopting RPA can reduce
operational costs by up to 30%.
RPA works by using software robots to mimic human actions. These robots can log into applications, enter data,
and extract information. A study from McKinsey points out that businesses can automate nearly 60%
of their daily tasks using RPA. However, the implementation can come with challenges. Not all processes are suited for automation,
and selecting the right tasks is crucial for success. Some businesses experience setbacks when scaling their RPA efforts due to
improper training or planning.
Despite its advantages, businesses need to approach RPA implementation critically. There have been reports of over-reliance on automation,
leading to neglect in team development and oversight. Moreover, if not properly managed, RPA could create data security vulnerabilities.
Organizations must remain vigilant and ensure that they regularly assess the impact of these automated processes on their workforce and operations.
Key Components of Robotic Process Automation Solutions
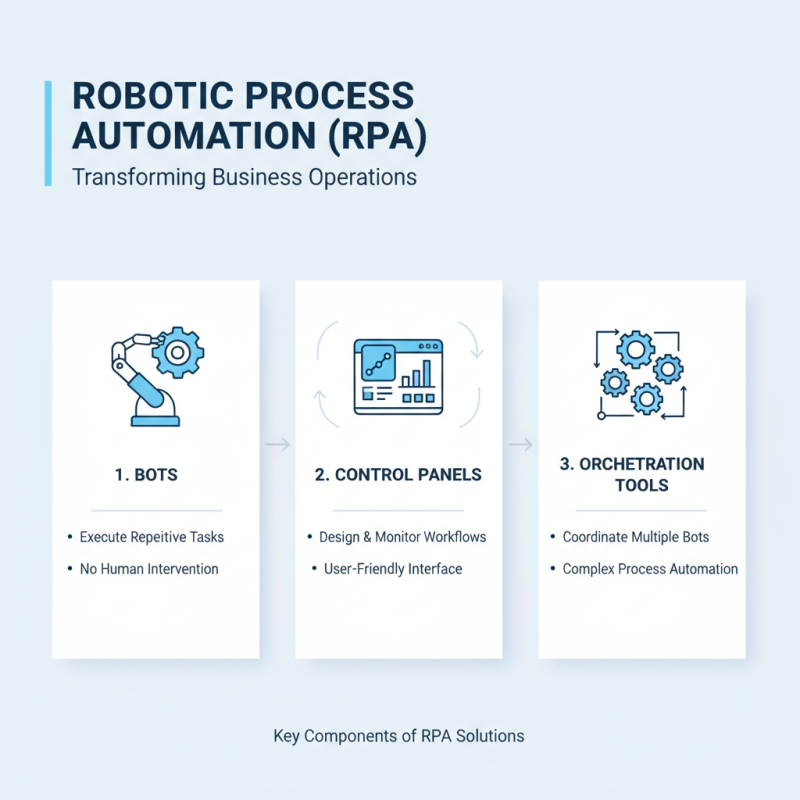
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is revolutionizing how businesses operate. The key components of RPA solutions include bots, control panels, and orchestration tools. Bots execute repetitive tasks quickly without human intervention. Control panels allow users to design and monitor automation workflows easily. Orchestration tools enable the coordination of multiple bots for complex processes.
According to a recent industry report, RPA can enhance productivity by up to 30% in some sectors. This improvement stems from the bots’ ability to work 24/7. However, an often-overlooked aspect is the need for proper oversight. Automation is not a set-and-forget solution. Regular checks are crucial to ensure bots perform as intended.
Tips: Always start with small processes before scaling up. It’s essential to measure the performance of RPA solutions regularly. Employees must be trained to adapt to automated systems. This ensures a smoother transition and reduces resistance to change.
While RPA offers great benefits, it does come with challenges. Some tasks may require judgment that bots cannot replicate. Therefore, organizations should evaluate which processes are best suited for automation. Balancing humans and bots can lead to optimal efficiency and better outcomes.
How Robotic Process Automation Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) simplifies various business processes. It uses software bots to automate repetitive tasks. These tasks might include data entry, invoice processing, or customer service inquiries. According to a report from Deloitte, 63% of organizations implement RPA to reduce operational costs. The efficiency gained can lead to increased productivity and better resource allocation.
When implementing RPA, the process usually begins with identifying repetitive tasks. This identification phase is crucial, as not all tasks are suitable for automation. A study by McKinsey found that up to 45% of current work activities could be automated using existing technologies. Next, the selected processes are mapped out in detail. This map serves as a blueprint for the RPA bot's operations.
After mapping, development starts. At this stage, software developers create the bots based on the process map. Testing follows to ensure accuracy. RPA can dramatically improve efficiency, but it requires proper oversight. Some organizations find themselves overwhelmed with managing the bots after deployment. Ensuring that the bots comply with the evolving business rules is essential for long-term success.
Robotic Process Automation Software Adoption by Industry
Benefits of Implementing Robotic Process Automation in Businesses

Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is transforming business operations in various sectors. One of the key benefits is enhanced efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can reduce human error. For instance, data entry and invoice processing are ideal for RPA. A machine works faster and more accurately than a person, which can save significant time.
Additionally, RPA supports scalability. As a business grows, so does the workload. RPA systems can easily adapt to increased demands without hiring more staff. This dynamic is crucial, especially for small and medium enterprises. However, implementing RPA is not without challenges. Employees may feel threatened by automation. Proper communication and training are essential to alleviate these concerns.
Cost savings are another advantage. Automating processes reduces operational costs over time. Yet, businesses must consider initial setup expenses. They should assess the return on investment carefully. Balancing automation with human oversight can create a more harmonious work environment. Finding this balance is critical for success in the long run.
Common Use Cases and Industries Leveraging RPA Technology
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) technology is reshaping many industries today. Businesses in finance are using it for automating repetitive tasks. This includes invoice processing and data entry. Such automation increases efficiency and reduces errors. It's common to find RPA in retail for inventory management as well. This allows companies to track stock levels dynamically.
Healthcare is another sector leveraging RPA. Administrative tasks like appointment scheduling and insurance verification are automated. This helps staff focus on patient care, not paperwork. Interestingly, while RPA can drive productivity, it can also present challenges. For instance, companies may face issues with integration. Training personnel to work alongside RPA can require significant investment.
Manufacturing is embracing RPA too. Quality control processes can be streamlined, enhancing production accuracy. However, this can lead to over-reliance on technology. Increased automation might create dependence, raising concerns about workforce impact. Each industry must consider the balance between efficiency and human creativity.
What is Robotic Process Automation Software and How Does It Work? - Common Use Cases and Industries Leveraging RPA Technology
| Use Case | Industry | Benefits | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invoice Processing | Finance | Time savings, error reduction | Data extraction, validation |
| Customer Onboarding | Banking | Faster processing, improved customer experience | Form filling, document verification |
| Order Processing | E-commerce | Increased efficiency, lower costs | Integration with ERP systems, status updates |
| HR Management | Human Resources | Streamlined processes, better compliance | Talent acquisition automation, employee data management |
| Claims Processing | Insurance | Reduce processing time, enhance accuracy | Data entry, approval workflows |
Related Posts
-

Why Are Robotic Process Automation Tools Essential for Business Efficiency
-

What is Robot Technology and How is it Transforming Our Lives Today
-
2025 How to Master Advanced Robotics: Explore Trends, Tips, and Techniques
-

How to Choose the Best Manufacturing Robots for Your Business?
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Cobot Robots in Modern Manufacturing
-

Top 10 Reasons to Choose Cobot Robots for Your Business Efficiency
